The biggest lockdown in the history of mankind had to be implemented by the government of India. There are no international travels happening, no road or rail traffic in India and no one on the streets. The second-largest population in the world has been forced to stay indoors for 21 days by the smallest of the microorganisms in the world.

But is this still enough to fight this battle with the highly-infectious deadly disease – COVID-19?
There are several factors that make this battle different & crucial for the future of this country. However, in spite of all health infrastructure, it’s strengths and limitations, do we really have a chance to survive?
To understand why this all is being done, you need to first understand how our body’s immune system work. Then we’ll take a close look at what exactly happens when coronavirus attacks your body.
After that, we’ll look at the future of India, what’s happening, how to prevent this crisis and win the battle against COVID-19.
You’ll learn
- What is the immune system?
- What are white blood cells – function and types
- What is an immune response?
- The difference in Immune response: Bacteria vs Virus
- How does coronavirus attack your body?
- How dangerous is Coronavirus without symptoms?
- Why is coronavirus spreading so fast?
- How to eliminate coronavirus
- What is the need of the hour to prevent coronavirus
What is an Immune System?
The immune system is a body’s defense mechanism. It’s essential for your health, fighting bacteria & viruses and staying free from infections. It’s made out of white blood cells and is spread throughout the whole body.
White Blood Cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes, circulate in your blood and lymphatic vessels. Their main function is to fight viruses, bacteria, and any invaders. When they find an invader, they rush in to fight and destroy it (1).
They’re produced by bone marrow constantly and they live a lifespan from 13 to 20 days, after which time they are destroyed in the lymphatic system. They’re stored throughout your body in many places such as (2):
- Thymus (A gland in upper chest in the center behind the chest bone which stays active till puberty)
- Spleen (an organ in the upper left part of the abdomen)
- Bone marrow (the spongy tissue inside some of your bones)
- Lymph nodes (small glands that filter lymph, the clear fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system)
There are also two main types of white blood cells, which we’ll look at next.
Phagocytes – These’re your main fighters. When they find an invader – virus or bacteria – they surround it and eat it (3).
Lymphocytes – This type of white blood cell keeps a log of your previous invaders. That way, when they attack your body again, it recognizes it and destroys it more efficiently (4).
These are the two main types of fighters – white blood cells. But what actually happens when your body is under attack?
The Immune Response
An immune response is a response of your body to invaders. These can be parasites such as viruses or bacteria. Let’s take a deeper look at what exactly happens when your body is under attack.
How Does Bacteria Attack Your Body?
Bacteria are small, single-celled organisms. There are life processes happening inside their bodies and consist of DNA, membrane, and cytoplasm (4). There’re many ways bacteria can get to your body. One way is when you’re cut.

When you’re cut or there’s any break in the skin, bacteria can use it as a way to get to your body. It can enter the body through the food or the air you breathe.
After bacteria is in your body, your immune system can detect it. However, some bacteria are very sophisticated, so sometimes they can go unnoticed by your body.
When it’s in your body, it starts replicating itself by cell division(5). Sometimes, your body can detect bacteria early and destroy it. However, there’re times when it can’t. That’s when antibiotics come to help.
Antibiotics kill or stop the replication process of bacteria, so your body can have time to get rid of what’s left (6).
How Does Virus Attack Your Body?
Viruses are a lot smaller than bacteria. They’re made of DNA or RNA enclosed inside a coat of protein. There’re no processes happening, on its own virus doesn’t do anything. It just exists (7).

Let’s now take a little bit deeper look at how can viruses work.
You can imagine coronavirus or any other virus as a message in a bottle. It goes through your body and gets picked up by your body’s cell. It reads its message – genetic material – and reproduction of viruses inside the cell’s body starts happening (8).
There can be thousands of copies inside the cell happening. Once the new viruses are made, they leave the cell by destroying them. Then they’ll continue to spread out through your body.
Sometimes your body catches it early by T lymphocytes and destroys it immediately (9). However, sometimes if your immune system is weakened, your body detects it when it’s too late.
You need to be very careful because there’s no cure for the virus. However, there’re some antiviral drugs that can help inhibit the reproduction of viruses, but they don’t destroy them (10). Your body is on its own in tackling infections caused by viruses.
How Does Coronavirus Attack Your Body?
The virus is spread by droplets from sneeze or cough. It gets to your body through your nose or mouth or eyes. Once when it’s in your body it continues to stay in your throat for some time.
There the coronavirus attacks your cells. That’s why one of the first symptoms of coronavirus is a sore throat (11). After they’re reproduced in your throat, they continue down through your airways to your lungs.
It causes inflammation down there, which can make it more difficult for the lungs to function properly. It can also cause swelling, which makes it much more difficult for oxygen to get into your lungs. The swelling and decreased oxygen flow can cause your lungs to fill in with thick and viscous fluid and dead cells (12).
When it’s very severe, you may need to be put on breathing support also called a ventilator. In some cases, your lungs are filled with so much fluid, that no breathing support can help you and you die.
Coronavirus Without Symptoms
Sometimes when your cells get infected, the virus doesn’t start to replicate. It just mixes up the genetics of the cell. Then the cell starts to reproduce with these genetic changes inside of it.
This can happen because of the many reasons such as having a strong immune system. That’s why some people with coronavirus are asymptomatic – without symptoms. The virus knows that your immune system is very strong and would destroy it immediately (13).
So, it waits for the perfect opportunity when your immune system is weakened. This can be also caused by stress or physical activity. Then this opportunistic virus may strike and start attacking the infected cells.
However, just because you’re asymptomatic or without any signs or symptoms of infection, it doesn’t mean you can’t infect others. You can still carry the infection and transmit it to others even when you are not aware that you are walking bomb of these viruses sparking others with this contagious infection.
Why Is Coronavirus Spreading So Fast?
There have been many scares about coronavirus in recent times. But what makes it so scary? Why are the numbers of infected people skyrocketing so fast?
It has everything to do with the way it’s spread. Coronavirus is extremely infectious. Just as little as one droplet is enough to make you infected. The worst people are people with no symptoms – asymptomatic.
These individuals don’t even know they have it and spread it all around. On average, a person with coronavirus infects 2 – 3 people. However, this number is drastically higher when a person doesn’t know he is infected i.e., asymptomatic people.
The worst part is, that the number of infected people rises exponentially. That means that these numbers can rise to 180 million infected people and more than 45 million deaths without proper interventions.

How to Save India And Fight Coronavirus
India, unlike some countries, has a very young population. The average age in India is 27 years, which is very young. This is good, because young people are more resistant to coronavirus than elderly, as you can see from the chart below.

However, this doesn’t mean you can’t get infected when you’re young. You can always be an active career of the infection & infect so many other people without your knowledge. You need to strictly follow recommendations and interventions for preventing coronavirus to curb the spread. Most importantly, social distancing by avoiding the source of coronavirus – people.
The Initial Lockdown
The government of India has proactively started a 21 days lockdown a few days ago. It’s the biggest lockdown in the history of humans. All international travels have been stopped; no trains are traveling in the country. All the shops and factories have been closed and people must stay at home.
This may seem drastic, however, it’s essential for the prevention of spreading coronavirus. Fortunately, this lockdown started early, with just 300 cases as opposed to Italy (9,000) or the USA (11,000).
However, lockdown may be a great step for decreasing the number of infected people by breaking the chain of transmission, but it doesn’t have to help that much with eliminating the virus in infected people.
Why Initial Lockdown Isn’t Enough?
Lockdown is one of the most important things to decrease the spread of the virus. But does it help eliminate it?
When people are at home, there’s an exponentially lower chance of catching coronavirus. But what about infected people? Well… They stay infected and infect others around them.
This is the biggest problem in India right now and the solution is simple but not easy to execute. The way to eliminate coronavirus is to start testing, testing, and testing.
When you start testing people and detecting the virus in them, you start decreasing their exposure to healthy people by bringing them in quarantine. However, as we said earlier, on average, an infected person infects 2 – 3 people.
So, if we want to eliminate it completely, we need to trace all people who have been in contact with an infected person and put them to quarantine. Then and only then, we’ll save humanity and eliminate this extremely-infectious deadly virus. But do we have enough testing kits to be able to do that?
The Shortage of Testing Kits in India

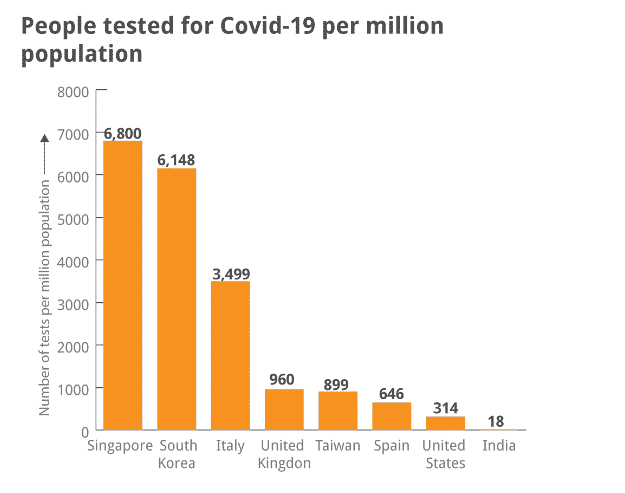
Testing may be the answer to eliminating coronavirus, but can we afford it? India tests around 1700 people daily and this number rises as you can see from the chart below.
BUT THIS IS NOT ENOUGH!
India is so far among the lowest ratios of testing in the world. One of the reasons is a shortage of testing kits. Below is a chart comparing India’s testing to other countries.

As you can see, India is extremely behind other countries. This is all because of the shortage of testing kits. There’s been delivered around 1 million testing kits so far. But this is very little for a country with more than 1.3 billion inhabitants.
When people can’t be tested, we don’t know if they’re infected or not. This leads to a huge spread of coronavirus in the country and around the world. But even if we had enough tests, would it help?
Hospitalization & Lack of Beds
Sooner or later, the number of infected people with coronavirus will rise. The problem is, can we take care of these people?
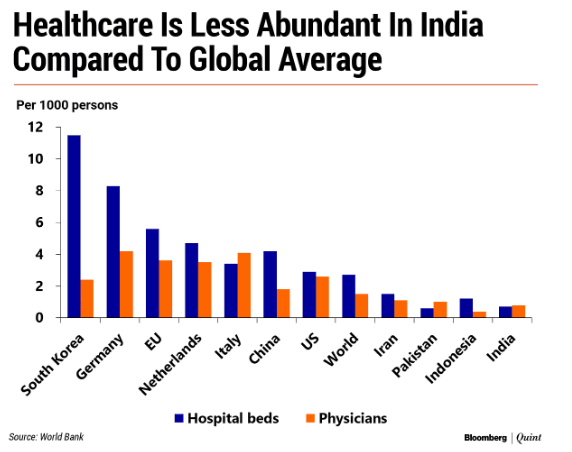
Most of the deaths from coronavirus aren’t because of the severity of the disease. Rather because of the lack of hospital beds and ICU (intensive care unit) beds.
Currently, India has 700000 hospital beds and 70000 ICU beds. This means there are only 0.7 beds per 1000 people, in comparison with the USA (2.9) and Italy (3.4). These two countries can’t handle it and there’re hundreds of deaths daily. How can we?

The lack of testing kits and beds in the hospital is a huge problem. But are there any solutions to these problems?
Well… The most important thing is to stop spreading it, that means take all the necessary steps to prevent it, which include:
- Wash your hands regularly
- Wear a facemask
- Clean and disinfect your environment
However, most people are doing all of these recommendations and still get sick. Why? Because they have weakened immunity. When you age, your body gets older and becomes weaker. So does your immunity system and so you’re more likely to catch coronavirus.
But this doesn’t mean that if you’re young you can’t get sick. Everyone’s immunity can get better and so can you prevent coronavirus. The best thing is, you can do it from home and it’s simple, fast & effective.
Boost Your Immunity & Protect Yourself
There’re many ways to support your immunity, which include:
- Eat healthily
- Regular exercise
- Drink a lot of water
- Quit smoking if you smoke
- Don’t drink a lot of alcohol
- Sleep at least 7 – 9 hours
Most of these are common sense, but if you’d have to choose, the most important is your diet. There’s nothing more important than your diet. It’s what gives you vitamins, nourishes your cells, heal your wounds, regenerates your body and makes you sustain a healthy body.
Your diet can make such a massive difference, that’s why you should start caring about what you’re putting in your mouth.
We have collected more than 15 food ideas, which will massively boost your immunity and can help decrease the chances of catching coronavirus or any other infectious disease. Here they’re:
Remember, you’re what you eat, and if you want to stay healthy, you need to eat healthily!
Stay informed, stay blessed & LiveLifemore!
Sources:
Role of White Blood Cells in Blood- and Bone Marrow-Based Autologous Therapies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6077567/
What are the organs of the immune system?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279395/
Phagocytosis: A Fundamental Process in Immunity
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5485277/
Lymphocytes and the Cellular Basis of Adaptive Immunity
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26921/
Introduction to Bacteriology
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8120/
Growth and Reproduction of Bacteria
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2051730/
Antibiotics
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535443/
Viruses: Structure, Function, and Uses
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21523/
T Cell Responses to Viral Infections – Opportunities for Peptide Vaccination
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3997009/
Approved Antiviral Drugs over the Past 50 Years
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4978613/
An Outbreak of Human Coronavirus OC43 Infection and Serological Cross-reactivity with SARS Coronavirus
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2095096/
Pulmonary pathological features in coronavirus associated severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1770245/

Coronavirus, the deadly disease which will destroy the human race.
But is that really true or people are just scared? Coronavirus has spread to more than 100 countries now (1). It’s everywhere around the world and it infected more than 255.000 people and caused deaths to thousands (2).

However, did you know that more than 80% of infected people recovered without hospitalization (3)? Although there’s no medication to corona yet, most of the people have only mild symptoms and get over it.
But, this doesn’t mean there’s no risk and you should certainly follow steps to prevent it. Today, you’ll learn everything about coronavirus and how to prevent it. You’ll learn
1. What is coronavirus
2. The symptoms of coronavirus
3. Who is at risk?
4. The prevention of coronavirus
5. Natural plants for better immunity
What is coronavirus?
SARS-CoV-2 is a new type of coronavirus which causes COVID-19. It first appeared in China in December 2019, but now it’s spread all around the globe. It causes respiratory illness in humans and animals. All coronaviruses are zoonotic, which means they first developed in animals.

Then, a person got infected and spread it all around. Now, more than 215 thousand people are infected and more than 8 thousand people are dead.
Coronavirus is spreading immensely fast. This is because of its symptoms and the way it spreads – by the respiratory droplets. This is basically everything wet, which moves when you sneeze or cough.
 The symptoms of coronavirus aren’t always the same. They vary from person to person. They may appear very late when you have already infected other people. Some people don’t even know they have coronavirus. The symptoms of COVID-19 are usually mild and progress slowly.
The symptoms of coronavirus aren’t always the same. They vary from person to person. They may appear very late when you have already infected other people. Some people don’t even know they have coronavirus. The symptoms of COVID-19 are usually mild and progress slowly.
The most common symptoms of COVID-19 are:
• High temperature or fever
• Shortness of breath
• Cough
• Fatigue
However, symptoms aren’t the only reason for its fast spread.
It’s very infectious, just one drop can infect you. It’s very dangerous and you must be careful, especially if you’re at increased risk. We’ll talk more about people who are at increased risk in the next section.
Who is at risk?
The answer is everybody. Whether you’re a woman or man, old or young, you’re at risk.
 However, some people have a higher risk of getting it.
However, some people have a higher risk of getting it.
These include people who are:
1. 70+ years old
2. Having long-term medical condition – diabetes, lung disease, heart disease
3. Having a weakened immune system
4. Pregnant
All of these risk factors make you weaker and more susceptible to catching it. Therefore, you should try to minimize this risk, which you’ll learn how in the next section.
How to Prevent Coronavirus
Catching COVID-19 can be easy, that’s why you have to be consistent with the prevention. We’ll look at couple of easy ways to prevent coronavirus.
If you implement all of them into your life, your chances of catching coronavirus decrease drastically.
If you want to prevent coronavirus you should:
1.Wash Your Hands Regularly
The most important thing in preventing COVID-19 is washing your hands. Most of the time, coronavirus gets on to your hands. This is because you touch everything with your hands – door handle, food, buttons in the elevator.

Therefore, it’s very important to clean coronavirus from your hands. Unfortunately, most people wash their hands wrongly.
Let’s look at 5 steps to wash your hands properly (4):
1. Wet your hands Turn on the water (ideally with your forearm) and wet your hands. Then turn off the tap and apply soap.
2. Lather your hands by rubbing soap and your hands together. Be sure to cover all areas of your hands. Start with palms and fingers, continue with thumbs and back of your hands.
3. Scrub your hands This step is very important, you need to scrub your hands for at least 30 seconds.
4. Rinse your hands under clean running water.
5. Dry your hands with a clean towel.
Repeat this process 2 times. Most people wash their hands just a few seconds. This can lead to not cleaning up bacteria and viruses from your hands and catching COVID-19.
However, it’s also very important how regularly you wash your hands.
You must wash your hands:
1. Before, during and after preparing food
2. Before eating anything
3. After using the toilet
4. After blowing your nose, sneezing or couching
5. After touching or feeding animals
People are constantly looking for other ways to prevent coronavirus. However, it all starts with washing your hands. It’s the most important thing and you need to start taking it seriously.
2.) Avoid Close Contact with People
This applies mostly to the younger generation. There’s quarantine almost everywhere, so people aren’t at work and kids aren’t at school. This is mostly to prevent the spreading of coronavirus.
Unfortunately, many people confuse it with holidays. They go and with their friends and are around people all the time.

It’s not only inappropriate but also very risky. All it takes is one drop, cough or sneeze and you may be infected.
However, when you need to go out, for whatever important reason, have at least something to cover up your mouth. Having a respirator is the best option, it can block out up to 95% of airborne particles. It can even filter out bacteria and viruses (5).
Unfortunately, there’re almost any respirators left. However, this doesn’t mean you can’t use a face mask or anything to cover up your mouth and nose.
Remember, everything which can cover up your mouth and nose is better than nothing, whether it’s a scarf or homemade face mask.
Respect all of the regulations, minimize your contact with people, protect your mouth & nose and stay healthy.
3.) Get Enough Sleep
Insufficient sleep is a big problem in today’s world. However, did you know that sleep can impact your immune system?
When you sleep your body produces and releases cytokines. Cytokines are a type of protein, which targets inflammation and infection. They’re responsible for effective immune system response (6).
But, if you don’t sleep enough, you’re producing fewer cytokines and increasing your risk of getting ill.
Chronic sleep loss can even make the flu vaccine less effective by reducing your body’s ability to respond. You are also shortening your life and increasing your chances of dying prematurely by 12% (7).
There’s also a problem with melatonin production when you don’t get adequate sleep. Melatonin is a hormone, which is produced when you sleep. It is released before you go to sleep and during sleep.

That’s why people with irregular sleeping schedules have a problem falling asleep. Melatonin doesn’t know when to release so you have hard time falling asleep.
However, melatonin plays also a role in the immune system too. It helps your body differentiate between normal cells in your body and bacteria or viruses. It also helps with triggering immune system response (8).
Having insufficient levels of melatonin can put you at the risk of being sick. Go to sleep early, sleep regularly for at least 8 hours every night and boost your immunity.
4.) Stress Management
Whether you believe it or not, stress has a big impact on your health. When you are in stress, your body is releasing corticosteroid. It’s a hormone that suppresses the effectiveness of your immune system (9).

Another thing is your response to stress. Most of the people are in stress because of some difficulties in their lives. Some of them want to just feel free and untroubled, so they reach for alcohol or a cigarette.
However, there’re also medical problems linked to stress.
Hypertension is very closely linked to high levels of stress. It increases your risk of getting heart attack or stroke and shortens your life.
All of these factors together contribute to weakening your immune system and making you more vulnerable to coronavirus. Try to balance your life, get enough rest, have some me-time and feel a lot better.
5.) Strengthen Your Immune System
Another risk factor for catching COVID-19 is a weakened immune system. When you feel great and your immune system is strong, it doesn’t mean you can’t strengthen it even more.
Diet and exercise can help you with all of that. Become stronger, get more vitamins and be healthier.
Many people make excuses all the time that they don’t have time to exercise. Well, not that you’re in quarantine you have more time for it.
You don’t have to go to the gym or life weight. Start light with some push-ups, squats, and sit-ups. Train with your bodyweight and develop strength and improve your immune system (10). This improves your resistance to coronavirus.

Another very important thing is diet. You are what you and that’s why if you want to stay healthy, you must eat healthy.
Let’s look at the top 5 foods you must include in your diet to strengthen your immune system.
6.) Citrus Fruits
Usually, when you catch a cold, the first thing you do is to take vitamin C. It’s logical. Vitamin C boosts the production of white cells which in turn boosts immunity (11).
When deciding on foods that boost your immunity, citrus fruits should be the number one priority.
The most common ones are:
1. Grapefruit
2. Oranges
3. Lemons
4. Tangerine
5. Lime
Your body doesn’t produce vitamin C, so it’s important to include these fruits in your diet daily. Just one medium orange is all you need for daily recommended vitamin C intake (12).

a.) Broccoli
Broccoli is a superb nutritious vegetable. It contains both vitamins and minerals. Packed with antioxidants, fiber and vitamin C, A and E, it’s one of the healthiest vegetables out there.
However, if you want to benefit from all of these nutrients as much as possible, you have to cook it as little as possible. The best option is to not cook it at all.
Broccoli contains more than 84% of vitamin C (13). Include broccoli to your diet and boost your immunity tremendously.

b.) Ginger
Ginger is a great ingredient for helping with your immune system. It can help you decrease inflammation and improve sore throat. It also decreases chronic pain and lowers your cholesterol levels.
Gingerol, which are bioactive substances in fresh ginger, can help you lower the risk of infections. Ginger inhibits the growth of many different bacteria (14).
It’s especially good against viruses which cause respiratory infections, such as coronavirus (15) Include it in your diet, make yourself a tea and enjoy its benefits.

c.) Almonds
Nuts are great for your immune system and overall well-being. Especially almonds, which deliver a massive amount of nutrients. They are among the world’s best sources of vitamin E (16).
Vitamin E is key to the healthy immune system, lowering heart disease and decreasing the risk of cancer.
Eat a half-cup serving of almonds daily. This will provide you with 100% recommended daily amount of vitamin E.

d.) Green Tea
Green tea is considered to be the healthiest beverage on the planet (17). It’s packed with antioxidants and nutrients which are massively beneficial for your body.
It decreases the risk of getting cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and strengthen your immunity system (18).
Green tea has catechins, which are nutrients that kill bacteria and viruses (19).
Replace your fruit tea with green tea, improve your immunity and decrease the risk of chronic disease.

Natural Plants for Better Immunity
“Let food be thy medicine, and medicine be thy food”
Natural treatment is very beneficial for you and your body. It has been around for millenniums and was the first method of healing. It’s tested by Mother Earth and used around the world to treat medical conditions.
There’re three plants below, which are very common and can be beneficial for strengthening your immunity or overcoming the disease.
a.) Peppermint
Peppermint is an aromatic herb, which has been used for a thousand years for its pleasant, minty taste and health benefits.
Peppermint can help you with headaches, migraines or digestive problems. But did you know that it can also strengthen your immune system?

Peppermint is very effective in killing bacteria and viruses (20). It also reduces several bacteria in your mouth and freshens your breath (21).
What’s even more breathtaking is that it can improve your sleep, which is another factor in your immunity.
Peppermint tea is an ideal drink before a bed because it relaxes your muscles and makes you fall asleep easier (22).
b.) Garlic
There’re many reasons why you should include garlic in your diet. It’s very nutritious, it has many vitamins & minerals and has very little calories.
However, it’s also great for your immunity and combating sickness. It’s especially good for the cold. One garlic a day can reduce the number of cold by incredibly 63% (23).
However, when you take a high dose of aged garlic extract, you can decrease your chances of catching flu by 61% (24).

Its minerals and vitamins are very beneficial for your health and immune system. You should include it in your diet, especially right now, when coronavirus is everywhere.
c.) Quercetin
Quercetin is a plant pigment, which belongs to flavonoids. Flavonoids are a group of plant compounds and are present in fruit, vegetables, and grains.
It’s very beneficial to your health and has been linked with reducing the risk of heart disease, cancer or inflammation (25).
Inflammation may be very dangerous. It can drastically decrease the effectiveness of your immune system and make it easier for viruses to attack you (26).

Quercetin also helps with healing your wounds and fighting bacteria and viruses. Try to include it in your diet, get some fruit and vegetables, make healthy salads, avoid junk food, drink green tea and stay healthy.
You’ll make yourself more resistant to coronavirus and won’t gain much fat during the quarantine.
Final thoughts
COVID-19 is a very infectious disease caused by SARS-CoV-2. It developed in animals and progressed to humans. Even though it started in China, now it’s all around the globe with more than 215k people infected.
Its symptoms aren’t always the same and are mild from the beginning. Then they slowly progress.
The most common symptoms are:
- Fever
- Coughing
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
It’s very infections and everybody should be careful. However, there’re people, who are at higher risk,
These include people who are:
1. 70+ years old
2. Having long-term medical condition – diabetes, lung disease, heart disease
3. Having a weakened immune system
4. Pregnant
You can drastically decrease your chances when you take steps to prevent it.
These steps are:
1. Regular and proper washing hands
2. Avoiding close contact with people
3. Strengthening your immune system
Stop putting other people at risk and stay home. Eat a lot of vitamins, wash your hands regularly and stay fit & healthy.
15.)Sources
Cardiovascular exercise training extends influenza vaccine seroprotection in sedentary older adults: the immune function intervention trial.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20121985
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 48
https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200308-sitrep-48-covid19.pdf?sfvrsn=16f7ccef_4
COVID-19 CORONAVIRUS OUTBREAK
https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
Vital Surveillances: The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19) — China, 2020
http://weekly.chinacdc.cn/en/article/id/e53946e2-c6c4-41e9-9a9b-fea8db1a8f51
When and How to Wash Your Hands
https://www.cdc.gov/handwashing/when-how-handwashing.html
Frequently Asked Questions about Personal Protective Equipment
https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/respirator-use-faq.html
Oranges, raw, all commercial varieties
https://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/fruits-and-fruit-juices/1966/2
Antibacterial effect of Allium sativum cloves and Zingiber officinale rhizomes against multiple-drug resistant clinical pathogens
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3609356/
Fresh ginger (Zingiber officinale) has anti-viral activity against the human respiratory syncytial virus in human respiratory tract cell lines.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23123794
Broccoli, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt
https://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/vegetables-and-vegetable-products/2357/2
Nuts, almonds [Includes USDA commodity food A256, A264]
https://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/nut-and-seed-products/3085/2
10 Proven Benefits of Green Tea
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/top-10-evidence-based-health-benefits-of-green-tea
Anti-infective properties of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a component of green tea.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23072320
The relationship between green tea and total caffeine intake and risk for self-reported type 2 diabetes among Japanese adults.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16618952
Cytokines and the immune response.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8813336
Sleep Duration and All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2864873/
Melatonin, immune function and aging
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1325257/
The effect of systemic corticosteroids on the innate and adaptive immune system in children with steroid responsive nephrotic syndrome.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26833050
[The treatment of respiratory ailments with essential oils of some aromatic medicinal plants].
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19039907
Antimicrobial efficacy of five essential oils against oral pathogens: An in vitro study.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24966732
A review of the bioactivity and potential health benefits of peppermint tea (Mentha piperita L.).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16767798
Preventing the common cold with a garlic supplement: a double-blind, placebo-controlled survey.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11697022
Supplementation with aged garlic extract improves both NK and γδ-T cell function and reduces the severity of cold and flu symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled nutrition intervention.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22280901
Health effects of quercetin: from antioxidant to nutraceutical.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18417116
Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5805548/